Installation on vSphere Cluster using Helm
This topic provides instructions for installing Portworx on a VMware vSphere cluster using the Portworx helm chart.
The following collection of tasks describe how to install Portworx:
- Create a monitoring ConfigMap
- Configure Storage DRS settings
- Grant the required cloud permissions
- Deploy Portworx using Helm
- Verify Portworx Pod Status
- Verify Portworx Cluster Status
- Verify Portworx Pool Status
- Verify pxctl Cluster Provision Status
Complete all the tasks to install Portworx.
Create a monitoring ConfigMap
Use this procedure only to install Portworx on a vSphere OpenShift cluster.
Enable monitoring for user-defined projects before installing the Portworx Operator. Use the instructions in this section to configure the OpenShift Prometheus deployment to monitor Portworx metrics.
To integrate OpenShift’s monitoring and alerting system with Portworx, create a cluster-monitoring-config ConfigMap in the openshift-monitoring namespace:
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cluster-monitoring-config
namespace: openshift-monitoring
data:
config.yaml: |
enableUserWorkload: true
The enableUserWorkload parameter enables monitoring for user-defined projects in the OpenShift cluster. This creates a prometheus-operated service in the openshift-user-workload-monitoring namespace.
Configure Storage DRS settings
Portworx does not support the movement of VMDK files from the datastores on which they were created.
Do not move the VMDK files manually or have any settings that would result in a movement of VMDK files.
To prevent Storage DRS from moving VMDK files, configure the Storage DRS settings as follows using your vSphere console.
From the Edit Storage DRS Settings window of your selected datastore cluster, edit the following settings:
-
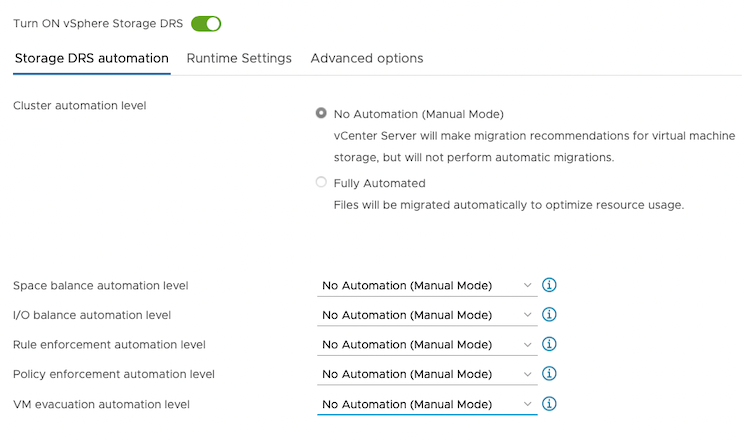
For Storage DRS automation, choose the No Automation (Manual Mode) option, and set the same for other settings, as shown in the following screencapture:
-
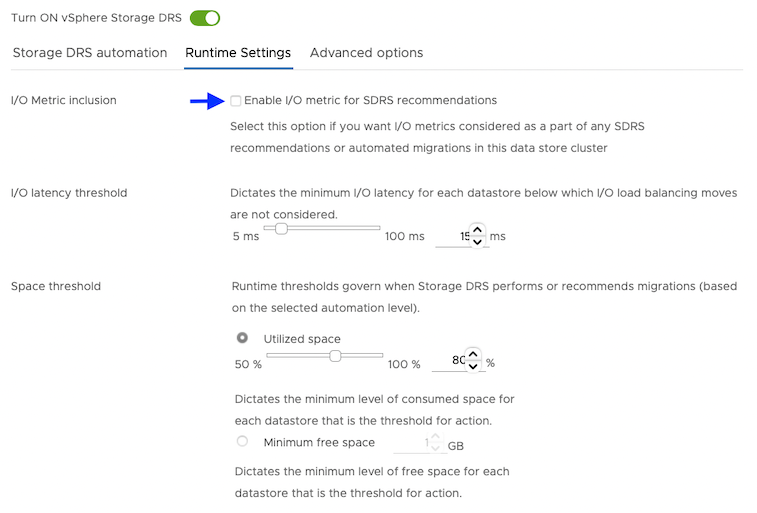
For Runtime Settings, clear the Enable I/O metric for SDRS recommendations option.
-
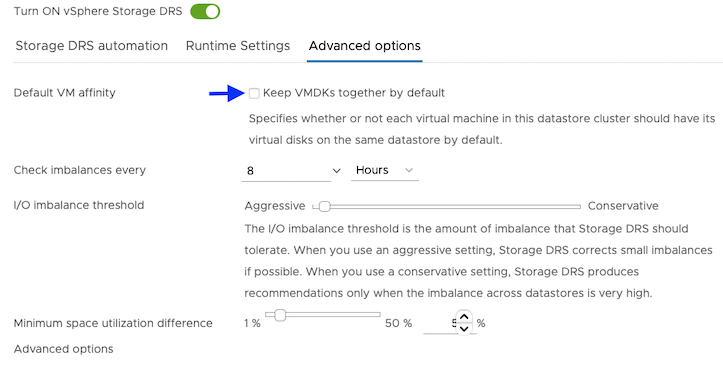
For Advanced options, clear the Keep VMDKs together by default options.
Grant the required cloud permissions
Grant the permissions that Portworx requires by creating a secret with the necessary user credentials:
- Using your vSphere console, provide Portworx with a vCenter server user account that has the following minimum vSphere privileges at vCenter datacenter level:
-
Datastore
- Allocate space
- Browse datastore
- Low level file operations
- Remove file
-
Host
- Local operations
- Reconfigure virtual machine
-
Virtual machine
- Change Configuration
- Add existing disk
- Add new disk
- Add or remove device
- Advanced configuration
- Change Settings
- Extend virtual disk
- Modify device settings
- Remove disk
If you create a custom role as above, make sure to select Propagate to children when assigning the user to the role.
Why selectPropagate to Children?In vSphere, resources are organized hierarchically. By selecting "Propagate to Children," you ensure that the permissions granted to the custom role are automatically applied not just to the targeted object, but also to all objects within its sub-tree. This includes VMs, datastores, networks, and other resources nested under the selected resource.
- Create a secret using the following steps.
- Kubernetes Secret
- Vault Secret
Retrieve the credentials from your own environment and specify them under the data section:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: px-vsphere-secret
namespace: portworx
type: Opaque
data:
VSPHERE_USER: <your-vcenter-server-user>
VSPHERE_PASSWORD: <your-vcenter-server-password>
-
VSPHERE_USER: to find your base64-encoded vSphere user, enter the following command:
echo '<vcenter-server-user>' | base64 -
VSPHERE_PASSWORD: to find your base64-encoded vSphere password, enter the following command:
echo '<vcenter-server-password>' | base64
After you update the template with your user and password, apply the spec:
oc apply -f <your-spec-name>
- Ensure that the ports 17001-17020 on worker nodes are reachable from the control plane node and other worker nodes.
For information on how to configure and store secret key for vSphere in Vault, see Vault Secret Provider.
- Ensure that the correct vSphere credentials are securely stored in Vault before Portworx installation.
- Ensure that the ports 17001-17020 on worker nodes are reachable from the control plane node and other worker nodes.
Deploy Portworx using Helm
This procedure assumes that Portworx is installed in the portworx namespace. If you want to install it in a different namespace, use the -n <px-namespace> flag.
-
To install Portworx, add the
portworx/helmrepository to your local Helm repository.helm repo add portworx https://raw.githubusercontent.com/portworx/helm/master/stable/"portworx" has been added to your repositories -
Verify that the repository has been successfully added.
helm repo listNAME URL
portworx https://raw.githubusercontent.com/portworx/helm/master/stable/ -
Create a
px_install_values.yamlfile and add the following parameters.openshiftInstall: true
drives: 'type=thin,size=150'
envs:
- name: VSPHERE_INSECURE
value: 'true'
- name: VSPHERE_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef: null
name: px-vsphere-secret
key: VSPHERE_USER
- name: VSPHERE_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef: null
name: px-vsphere-secret
key: VSPHERE_PASSWORD
- name: VSPHERE_VCENTER
value: <your-vCenter-Endpoint>
- name: VSPHERE_VCENTER_PORT
value: <your-vCenter-Port>
- name: VSPHERE_DATASTORE_PREFIX
value: <your-vCenter-Datastore-prefix>
- name: VSPHERE_INSTALL_MODE
value: shared -
(Optional) In many cases, you may want to customize Portworx configurations, such as enabling monitoring or specifying specific storage devices. You can pass the custom configuration to the
px_install_values.yamlyaml file.note- You can refer to the Portworx Helm chart parameters for a list of configurable parameters and values.yaml file for configuration file template.
- The default clusterName is
mycluster. However, it's recommended to change it to a unique identifier to avoid conflicts in multi-cluster environments.
-
Install Portworx.
noteTo install a specific version of Helm chart, you can use the
--versionflag. Example:helm install <px-release> portworx/portworx --version <helm-chart-version>.helm install <px-release> portworx/portworx -n portworx -f px_install_values.yaml --debug -
Check the status of your Portworx installation.
helm status <px-release> -n portworxNAME: px-release
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Sep 26 05:53:17 2024
NAMESPACE: portworx
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Your Release is named "px-release"
Portworx Pods should be running on each node in your cluster.
Portworx would create a unified pool of the disks attached to your Kubernetes nodes.
No further action should be required and you are ready to consume Portworx Volumes as part of your application data requirements.
Verify Portworx Pod Status
Run the following command to list and filter the results for Portworx pods and specify the namespace where you have deployed Portworx:
- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
oc get pods -n <px-namespace> -o wide | grep -e portworx -e px
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
portworx-api-8scq2 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
portworx-api-f24b9 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
portworx-api-f95z5 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
portworx-kvdb-558g5 1/1 Running 0 3m46s xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
portworx-kvdb-9tfjd 1/1 Running 0 2m57s xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
portworx-kvdb-cjcxg 1/1 Running 0 3m7s xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
portworx-operator-548b8d4ccc-qgnkc 1/1 Running 0 5h2m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
portworx-pvc-controller-ff669698-62ngd 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
portworx-pvc-controller-ff669698-6b4zj 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
portworx-pvc-controller-ff669698-pffvl 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
prometheus-px-prometheus-0 2/2 Running 0 5h xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx-2qsp4 2/2 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx-5vnzv 2/2 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx-lxzd5 2/2 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
px-csi-ext-77fbdcdcc9-7hkpm 4/4 Running 0 3h19m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
px-csi-ext-77fbdcdcc9-9ck26 4/4 Running 0 3h18m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
px-csi-ext-77fbdcdcc9-ddmjr 4/4 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
px-prometheus-operator-7d884bc8bc-5sv9r 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
kubectl get pods -n <px-namespace> -o wide | grep -e portworx -e px
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
portworx-api-8scq2 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
portworx-api-f24b9 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
portworx-api-f95z5 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
portworx-kvdb-558g5 1/1 Running 0 3m46s xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
portworx-kvdb-9tfjd 1/1 Running 0 2m57s xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
portworx-kvdb-cjcxg 1/1 Running 0 3m7s xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
portworx-operator-548b8d4ccc-qgnkc 1/1 Running 0 5h2m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
portworx-pvc-controller-ff669698-62ngd 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
portworx-pvc-controller-ff669698-6b4zj 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
portworx-pvc-controller-ff669698-pffvl 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
prometheus-px-prometheus-0 2/2 Running 0 5h xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx-2qsp4 2/2 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx-5vnzv 2/2 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx-lxzd5 2/2 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
px-csi-ext-77fbdcdcc9-7hkpm 4/4 Running 0 3h19m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 <none> <none>
px-csi-ext-77fbdcdcc9-9ck26 4/4 Running 0 3h18m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
px-csi-ext-77fbdcdcc9-ddmjr 4/4 Running 0 3h20m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 <none> <none>
px-prometheus-operator-7d884bc8bc-5sv9r 1/1 Running 0 5h1m xx.xx.xxx.xxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 <none> <none>
Note the name of a px-cluster pod. You will run pxctl commands from these pods in Verify Portworx Cluster Status.
Verify Portworx Cluster Status
You can find the status of the Portworx cluster by running pxctl status commands from a pod.
Enter the following command, specifying the pod name you retrieved in Verify Portworx Pod Status:
- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
oc exec <px-pod-name> -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl status
Defaulted container "portworx" out of: portworx, csi-node-driver-registrar
Status: PX is operational
Telemetry: Disabled or Unhealthy
Metering: Disabled or Unhealthy
License: Trial (expires in 31 days)
Node ID: 24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
IP: xx.xx.xxx.xxx
Local Storage Pool: 1 pool
POOL IO_PRIORITY RAID_LEVEL USABLE USED STATUS ZONE REGION
0 HIGH raid0 25 GiB 33 MiB Online default default
Local Storage Devices: 1 device
Device Path Media Type Size Last-Scan
0:0 /dev/sda STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD 32 GiB 10 Oct 22 23:45 UTC
total - 32 GiB
Cache Devices:
* No cache devices
Kvdb Device:
Device Path Size
/dev/sdc 1024 GiB
* Internal kvdb on this node is using this dedicated kvdb device to store its data.
Metadata Device:
1 /dev/sdd STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD 64 GiB
Cluster Summary
Cluster ID: px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Cluster UUID: 482b18b1-2a8b-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Scheduler: kubernetes
Nodes: 3 node(s) with storage (3 online)
IP ID SchedulerNodeName Auth StorageNode Used Capacity Status StorageStatus Version Kernel OS
xx.xx.xxx.xxx 24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 Disabled Yes(PX-StoreV2) 33 MiB 25 GiB Online Up (This node) 3.2.0-28944c8 5.4.217-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
xx.xx.xxx.xxx 1e89102f-0510-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 Disabled Yes(PX-StoreV2) 33 MiB 25 GiB Online Up 3.2.0-28944c8 5.4.217-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
xx.xx.xxx.xxx 0c99e1f2-9d49-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 Disabled Yes(PX-StoreV2) 33 MiB 25 GiB Online Up 3.2.0-28944c8 5.4.217-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
Global Storage Pool
Total Used : 99 MiB
Total Capacity : 74 GiB
kubectl exec <px-pod-name> -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl status
Defaulted container "portworx" out of: portworx, csi-node-driver-registrar
Status: PX is operational
Telemetry: Disabled or Unhealthy
Metering: Disabled or Unhealthy
License: Trial (expires in 31 days)
Node ID: 24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
IP: xx.xx.xxx.xxx
Local Storage Pool: 1 pool
POOL IO_PRIORITY RAID_LEVEL USABLE USED STATUS ZONE REGION
0 HIGH raid0 25 GiB 33 MiB Online default default
Local Storage Devices: 1 device
Device Path Media Type Size Last-Scan
0:0 /dev/sda STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD 32 GiB 10 Oct 22 23:45 UTC
total - 32 GiB
Cache Devices:
* No cache devices
Kvdb Device:
Device Path Size
/dev/sdc 1024 GiB
* Internal kvdb on this node is using this dedicated kvdb device to store its data.
Metadata Device:
1 /dev/sdd STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD 64 GiB
Cluster Summary
Cluster ID: px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Cluster UUID: 482b18b1-2a8b-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Scheduler: kubernetes
Nodes: 3 node(s) with storage (3 online)
IP ID SchedulerNodeName Auth StorageNode Used Capacity Status StorageStatus Version Kernel OS
xx.xx.xxx.xxx 24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx username-vms-silver-sight-3 Disabled Yes(PX-StoreV2) 33 MiB 25 GiB Online Up (This node) 3.2.0-28944c8 5.4.217-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
xx.xx.xxx.xxx 1e89102f-0510-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx username-vms-silver-sight-0 Disabled Yes(PX-StoreV2) 33 MiB 25 GiB Online Up 3.2.0-28944c8 5.4.217-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
xx.xx.xxx.xxx 0c99e1f2-9d49-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx username-vms-silver-sight-2 Disabled Yes(PX-StoreV2) 33 MiB 25 GiB Online Up 3.2.0-28944c8 5.4.217-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
Global Storage Pool
Total Used : 99 MiB
Total Capacity : 74 GiB
Status displays PX is operational when the cluster is running as expected. If the cluster is using the PX-StoreV2 datastore, the StorageNode entries for each node displays Yes(PX-StoreV2).
Verify Portworx Pool Status
This procedure is applicable for clusters with PX-StoreV2 datastore.
Run the following command to view the Portworx drive configurations for your pod:
- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
oc exec <px-pod> -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl service pool show
Defaulted container "portworx" out of: portworx, csi-node-driver-registrar
PX drive configuration:
Pool ID: 0
Type: PX-StoreV2
UUID: 58ab2e3f-a22e-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
IO Priority: HIGH
Labels: kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=username-vms-silver-sight-3,kubernetes.io/os=linux,medium=STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD,beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,iopriority=HIGH
Size: 25 GiB
Status: Online
Has metadata: No
Balanced: Yes
Drives:
0: /dev/sda, Total size 32 GiB, Online
Cache Drives:
No Cache drives found in this pool
Metadata Device:
1: /dev/sdd, STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD
kubectl exec <px-pod> -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl service pool show
Defaulted container "portworx" out of: portworx, csi-node-driver-registrar
PX drive configuration:
Pool ID: 0
Type: PX-StoreV2
UUID: 58ab2e3f-a22e-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
IO Priority: HIGH
Labels: kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=username-vms-silver-sight-3,kubernetes.io/os=linux,medium=STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD,beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,iopriority=HIGH
Size: 25 GiB
Status: Online
Has metadata: No
Balanced: Yes
Drives:
0: /dev/sda, Total size 32 GiB, Online
Cache Drives:
No Cache drives found in this pool
Metadata Device:
1: /dev/sdd, STORAGE_MEDIUM_SSD
The output Type: PX-StoreV2 ensures that the pod uses the PX-StoreV2 datastore.
Verify pxctl Cluster Provision Status
-
Access the Portworx CLI.
-
Run the following command to find the storage cluster:
- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
oc -n <px-namespace> get storageclusterNAME CLUSTER UUID STATUS VERSION AGE
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx 482b18b1-2a8b-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-dev-rc1 5h6mkubectl -n <px-namespace> get storageclusterNAME CLUSTER UUID STATUS VERSION AGE
px-cluster-378d7ae1-f4ca-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx 482b18b1-2a8b-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-dev-rc1 5h6mThe status must display the cluster is
Online. -
Run the following command to find the storage nodes:
- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
oc -n <px-namespace> get storagenodesNAME ID STATUS VERSION AGE
username-vms-silver-sight-0 1e89102f-0510-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-28944c8 3h25m
username-vms-silver-sight-2 0c99e1f2-9d49-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-28944c8 3h25m
username-vms-silver-sight-3 24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-28944c8 3h25mkubectl -n <px-namespace> get storagenodesNAME ID STATUS VERSION AGE
username-vms-silver-sight-0 1e89102f-0510-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-28944c8 3h25m
username-vms-silver-sight-2 0c99e1f2-9d49-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-28944c8 3h25m
username-vms-silver-sight-3 24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Online 3.2.0-28944c8 3h25mThe status must display the nodes are
Online. -
Verify the Portworx cluster provision status by running the following command.
Specify the pod name you retrieved in Verify Portworx Pod Status.- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
oc exec <px-pod> -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl cluster provision-statusNODE NODE STATUS POOL POOL STATUS IO_PRIORITY SIZE AVAILABLE USED PROVISIONED ZONE REGION RACK
0c99e1f2-9d49-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Up 0 ( 8ec9e6aa-7726-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx ) Online HIGH 32 GiB 32 GiB 33 MiB 0 B default default default
1e89102f-0510-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Up 0 ( 06fcc73a-7e2f-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx ) Online HIGH 32 GiB 32 GiB 33 MiB 0 B default default default
24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Up 0 ( 58ab2e3f-a22e-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx ) Online HIGH 32 GiB 32 GiB 33 MiB 0 B default default defaultkubectl exec <px-pod> -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl cluster provision-statusNODE NODE STATUS POOL POOL STATUS IO_PRIORITY SIZE AVAILABLE USED PROVISIONED ZONE REGION RACK
0c99e1f2-9d49-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Up 0 ( 8ec9e6aa-7726-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx ) Online HIGH 32 GiB 32 GiB 33 MiB 0 B default default default
1e89102f-0510-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Up 0 ( 06fcc73a-7e2f-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx ) Online HIGH 32 GiB 32 GiB 33 MiB 0 B default default default
24508311-e2fe-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Up 0 ( 58ab2e3f-a22e-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx ) Online HIGH 32 GiB 32 GiB 33 MiB 0 B default default default
What to do next
Create a PVC. For more information, see Create your first PVC.
(Optional) Update Portworx Configuration using Helm
To update the configuration of Portworx, modify the parameters in the px_install_values.yaml file specified during the Helm installation. This allows you to change the values of configuration parameters.
-
Create or edit the
px_install_values.yamlfile to update the desired parameters.vim px_install_values.yamlmonitoring:
telemetry: false
grafana: true -
Apply the changes.
helm upgrade <px-release> portworx/portworx -n <portworx> -f px_install_values.yamlRelease "px-release" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: px-release
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Sep 26 06:42:20 2024
NAMESPACE: portworx
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Your Release is named "px-release"
Portworx Pods should be running on each node in your cluster.
Portworx would create a unified pool of the disks attached to your Kubernetes nodes.
No further action should be required and you are ready to consume Portworx Volumes as part of your application data requirements. -
Verify that the new values have taken effect.
helm get values <px-release> -n <portworx>You should see all the custom configurations passed using the
px_install_values.yamlfile.