Expand your Storage Pool with Autopilot
Autopilot is a rule-based engine that responds to changes from a monitoring source. Autopilot allows you to specify monitoring conditions along with actions it should take when those conditions occur.
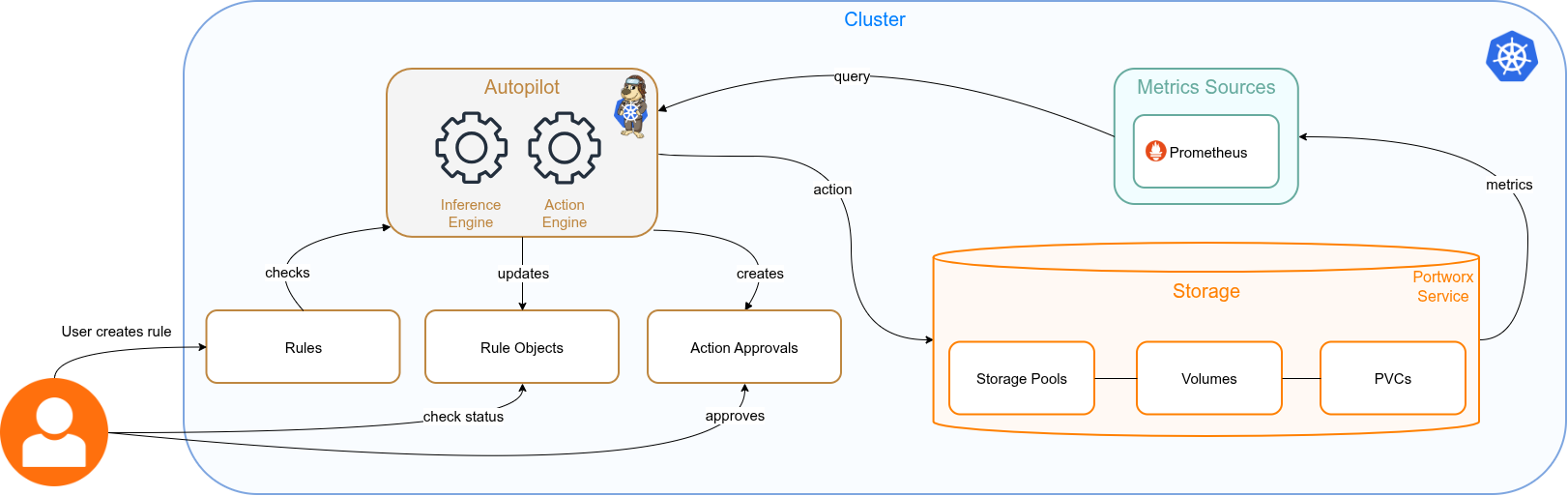
A user creates Portworx Autopilot rule. When an event occurs that is defined by an Autopilot rule, Autopilot can take a decision by fetching and using the metrics from the monitoring source configured on your cluster.
With Autopilot, your cluster can react dynamically without your intervention to events such as:
- Resizing PVCs when it is running out of capacity
- Scaling Portworx storage pools to accommodate increasing usage
- Rebalancing volumes across Portworx storage pools when they come unbalanced
Configuring and managing Autopilot with Portworx on Kubernetes cluster includes the following:
- Configure Autopilot with Portworx
- Customize Autopilot
- Configure Autopilot with PX-Security
- Upgrade Autopilot
Configure Autopilot with Portworx
Prerequisites
Ensure that your cluster has a running Prometheus so that Autopilot can fetch the metrics from it and take actions if the monitoring conditions are met.
- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
Autopilot requires a running OpenShift Prometheus instance in your cluster. If you don't have Prometheus configured in your cluster, refer to the Observability section to set it up.
After you have enabled OpenShift Prometheus, fetch the Thanos host, which is part of the OpenShift monitoring stack.
oc get route thanos-querier -n openshift-monitoring -o json | jq -r '.spec.host'
thanos-querier-openshift-monitoring.tp-nextpx-iks-catalog-pl-80e1e1cd66534115bf44691bf8f01a6b-0000.us-south.containers.appdomain.cloud
Configure Autopilot using the above route host to enable its access to Prometheus's statistics.
Autopilot requires a running Prometheus instance in your cluster. If you don't have Prometheus configured in your cluster, refer to the Observability section to set it up.
After you have Prometheus running, find the Prometheus service endpoint in your cluster. Depending on how you installed Prometheus, the precise steps to find this may vary. In most clusters, you can find a service named Prometheus:
kubectl get service -n portworx prometheus
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
prometheus LoadBalancer 10.0.201.44 X.X.X.0 9090:30613/TCP 11d
In the example above, http://prometheus:9090 becomes the Prometheus endpoint. Portworx uses this endpoint in the Autopilot Configuration section.
Why http://prometheus:9090 ?
prometheus is the name of the Kubernetes service for Prometheus in the portworx namespace. Since Autopilot also runs as a pod in the portworx namespace, it can access Prometheus using its Kubernetes service name and port.
Enable Autopilot with Portworx
Ensure that Autopilot is enabled in the StorageCluster specification as shown below:
kind: StorageCluster
spec:
autopilot:
enabled: true
Setting spec.autopilot.enabled: true in the StorageCluster specification enables Autopilot on the cluster.
Customize Autopilot
You can customize Autopilot by specifying configuration parameters to the Autopilot spec within your Portworx StorageCluster manifest. The following example shows how to customize Autopilot configuration to use custom the Prometheus URL and update the log level to debug based on your requirement.
- OpenShift
- Kubernetes
apiVersion: core.libopenstorage.org/v1
kind: StorageCluster
...
spec:
autopilot:
enabled: true
image: portworx/autopilot:1.3.14
providers:
- name: default
params:
url: https://<THANOS-QUERIER-HOST>
type: prometheus
args:
log-level: debug
apiVersion: core.libopenstorage.org/v1
kind: StorageCluster
...
spec:
autopilot:
enabled: true
image: portworx/autopilot:1.3.14
providers:
- name: default
params:
url: http://px-prometheus:9090 # If you using an external prometheus, update the url with external prometheus endpoint.
type: prometheus
args:
log-level: debug
Configure Autopilot with PX-Security
If you have to configure Autopilot with PX-Security using the Operator, you must modify the StorageCluster manifest. Add the following PX_SHARED_SECRET env var to the spec.autopilot:
autopilot:
...
env:
- name: PX_SHARED_SECRET
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: apps-secret
name: px-system-secrets
Upgrade Autopilot
To upgrade Autopilot, follow the appropriate procedure based on your setup:
To latest Autopilot image without upgrading Portworx
Portworx Operator takes care of updating all the components including autopilot based on the update strategy. If spec.autoUpdateComponents is set to Always in the STC, Portworx will check for update on regular interval and update the Autopilot image if new version is released.
To a custom Autopilot image without upgrading Portworx
To upgrade Autopilot to a custom image:
- Update the
configmap/px-versionswith the desired custom Autopilot image. - Add the
autoUpdateComponentsfield to the storage cluster specification:
kind: StorageCluster
spec:
autoUpdateComponents: Once
This will prompt the Portworx Operator to reconcile the Autopilot component and pull the latest image from the updated configmap.
Along With Portworx Upgrade without configmap
-
Delete the
configmap/px-versionsfile.When Portworx is upgraded, the Operator will automatically upgrade the installed components to the recommended versions.
-
Upgrade the Portworx image in the storage cluster specification to proceed with the upgrade.
Along With Portworx Upgrade with configmap
-
Download the latest Portworx version manifest:
curl -o versions.yaml "https://install.portworx.com/$<portworx-version>/version?kbver=$<kubernetes-version>&opver=$<operator-version>"Replace:
<portworx_version>with the Portworx version you want to use.<kubernetes-version>with the Kubernetes version you want to use.<operator-version>with the Operator version you want to use.
-
Update the px-versions configmap with the downloaded version manifest:
kubectl -n <px-namespace> delete configmap px-versions
kubectl -n <px-namespace> create configmap px-versions --from-file=versions.yaml -
Add the
autoUpdateComponentsfield to the storage cluster specification:kind: StorageCluster
spec:
autoUpdateComponents: OnceThis will prompt the Portworx Operator to reconcile all components and retrieve the latest images from the configmap if available, or download them from the manifest if not.