Tune performance
In its default configuration, Portworx attempts to provide good performance across a wide range of situations. However, you can improve your storage performance on your environment by configuring a number of settings and leveraging features Portworx offers. To get the most out of Portworx, follow the guidance provided in this article.
Configure the network data interface
You can provide Portworx with a specific network interface for data when you generate the spec as part of your installation. Portworx by Pure Storage recommends a network interface with a bandwidth of at least 10Gb/s and network latency below 5 milliseconds. If multiple NICs are present on the host, present a bonded interface to Portworx.
If you've already installed Portworx, you can update the network.dataInterface value of the install spec and reapply it.
Configure multiple NICs with LACP NIC Bonding
Portworx uses a single network interface for data traffic, which you define as the network.dataInterface in the StorageCluster spec. This interface handles all data traffic between Portworx nodes and applications. The interface can be either a single NIC or a bonded interface when multiple NICs are present on a node or host.
For optimal performance with bonded interfaces, ensure your Linux bonding configuration has the xmit_hash_policy set to layer3+4. The default value of layer2 will not effectively distribute traffic across multiple links. Without this setting, traffic between two hosts will only utilize a single network link, even when multiple links are available in the bond. This setting is critical to achieve the full bandwidth benefits of LACP bonding with Portworx.
For more information about bonding configuration options, refer to the Linux bonding documentation.
In earlier releases, Portworx used a single connection over the interface, which caused all network threads to contend for the single connection. This contention restricts load distribution and prevents full utilization of available bandwidth. With LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) NIC bonding support, Portworx can now create multiple parallel connections over the same interface, which significantly increases throughput by transmitting multiple data streams concurrently.
How to define a data network interface.
You can define the interface either during initial installation or by updating your existing storage cluster spec.
Option 1: During installation
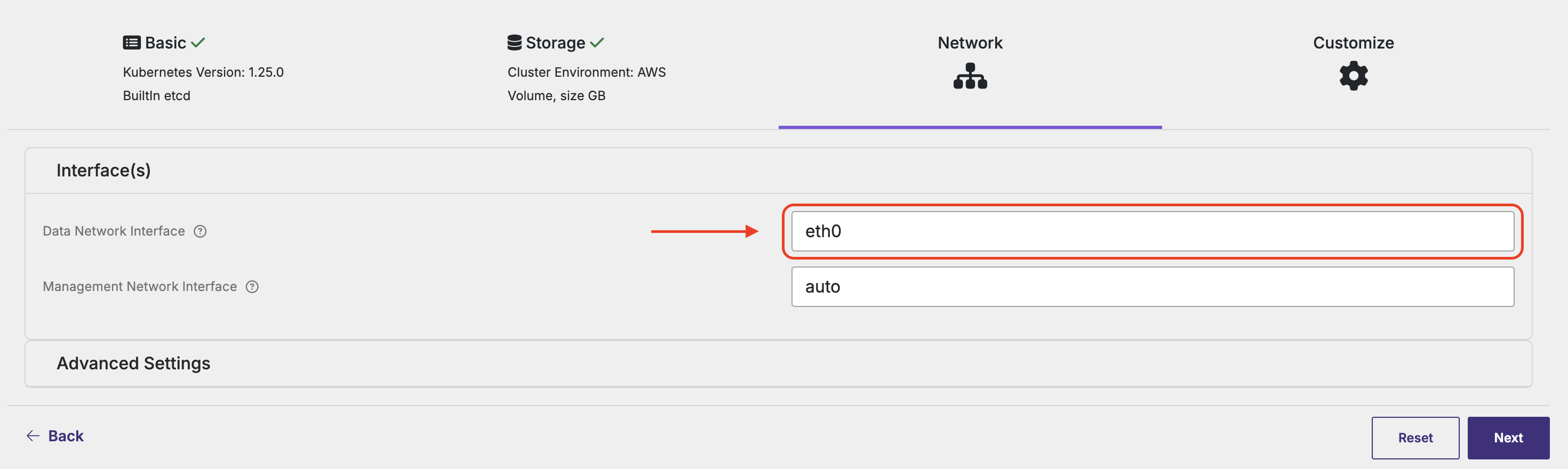
When generating the specs using the Portworx Central UI, choose the Customize options. Under the Network tab, you provide the network data interface as shown below.
Specify an interface name. If auto is specified, Portworx will select the first routable interface for management and network data interface.
Option 2: Updating an existing StorageCluster
On an already installed Portworx cluster, you can update the network.dataInterface value of the install spec and reapply it.
---
spec:
network:
dataInterface: eth0
---
Configure runtime option for parallel connections
Portworx creates multiple connections on the single address (i.e. interface). The number is defined by the cluster runtime options parameter connections_per_address, by default the value is 4.
This parameter is useful:
- When your nodes have only one NIC, and you want to reduce network contention.
- When using bonded interfaces that expose only one logical NIC.
- Or when you're running I/O-intensive workloads that generate a high volume of storage traffic.
To update the number of connections use the following command.
Only tune this parameter under guidance from Portworx Support or when you’ve identified a performance bottleneck via monitoring tools.
pxctl cluster options update --runtime-options "connections_per_address=2"
Note that a restart is required after you edit this parameter for Portworx to reinitialize connections.
Configure FUSE driver number of threads
Starting with Portworx 3.5, you can configure the number of threads used by the FUSE driver using the new tunable runtime option percentage_num_fpthreads. This option improves the performance of fast-path volumes by aligning the number of threads with available CPUs, based on workload characteristics and system resources.
Before you modify this value ensure FUSE driver is updated to version v3.5.0 or later.
If you're using a version earlier than 3.5.0 make sure to first update the Portworx Enterprise and follow below steps to update the px-fuse module:
- Take a backup of
/var/lib/osd/pxfs/latestdirectory. - Move the existing px-fuse module out of the way:
mv -f /var/lib/osd/pxfs/latest /var/lib/osd/pxfs/latest_backup - Reboot the node.
- After this the node will pull the latest px-fuse module matching the kernel.
Note: If you're using air-gap environment, you should run first run the pxfs-lib update daemon set to make sure latest kernel module archives are copied to the Portworx nodes.
Now, to modify the number of threads used for fast-path I/O, run the following command:
pxctl cluster options update --runtime-options percentage_num_fpthreads=xxx # Specify a value in the 0–100 range.
Or you can set it in the StorageCluster spec as follows:
apiVersion: core.libopenstorage.org/v1
kind: StorageCluster
metadata:
name: portworx
namespace: <px-namespace>
annotations:
portworx.io/misc-args: "-rt_opts percentage_num_fpthreads=50” # (Specify a value in the 0–100 range.)
This improvement is applicable only to fast-path volumes.
You can check the number of threads used for fast-path I/O by viewing the following file:
/sys/devices/pxd/pxd_num_fpthreads
Enable hyperconvergence
Use Stork to ensure your Pod is running on the same node in which the data resides.
Configure your cluster topology
When configured to be aware of your cluster topology, Portworx places replicas for high availability. Configure your cluster topology.
Define a VolumePlacementStrategy
StatefulSets and distributed NoSQL databases, such as Cassandra, require PVCs to be distributed across the cluster. Use Affinity/Anti Affinity rules along with topology labels to define relationships between PVCs.Define a VolumePlacementStrategy using affinity and anti-affinity labels to distribute volumes.
Adjust storage classes
To improve performance, adjust storage class parameters in the following ways:
-
Prioritize volume traffic by setting the
priority_io:field tohigh -
Choose the replication factor best suited to your high availability needs
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: px-storage-class
provisioner: pxd.portworx.com
allowVolumeExpansion: true
parameters:
repl: "2"
priority_io: "high"
nodiscard: "true"
Modify Portworx resource consumption
By default, Portworx consumes as little CPU and memory resources as possible. You can potentially improve performance by allocating more resources, allowing Portworx to use more CPU threads and memory. Do this by modifying the spec used to install Portworx based on your cluster architecture.
Disaggregated architecture
In disaggregated deployments with dedicated storage nodes, enable higher resource consumption by specifying the rt_opts_conf_high runtime option:
apiVersion: core.libopenstorage.org/v1
kind: StorageCluster
metadata:
name: px-cluster
namespace: <px-namespace>
spec:
image: portworx/oci-monitor:3.1.6
...
runtimeOptions:
rt_opts_conf_high: "1"
Hyperconverged architecture
In a non-disaggregated/hyperconverged architecture, where applications are running on the same host as storage, set threads based on the number of cores that can be allocated to Portworx. For example, if your host has 16 cores:
num_threads=16sets the total number of threads performing storage operations.num_io_threads=12sets the number of threads that can do IO operations out of the totalnum_threads. In general, IO threads should be 75% of total threads.num_cpu_threads=16sets the number threads that can do operations other than IO out of the total num_threads.
Configure these values as runtime options:
apiVersion: core.libopenstorage.org/v1
kind: StorageCluster
metadata:
name: px-cluster
namespace: <px-namespace>
spec:
image: portworx/oci-monitor:3.1.6
...
runtimeOptions:
rt_opts_conf_high: "1"
num_threads: "16"
num_io_threads: "12"
num_cpu_threads: "16"
To see more StorageCluster examples, visit the StorageCluster section of the documentation.