Synchronous Disaster Recovery
This topic explains how to install a stretched Portworx cluster and achieve synchronous disaster recovery (DR). It demonstrates how to failover and failback applications between two clusters.
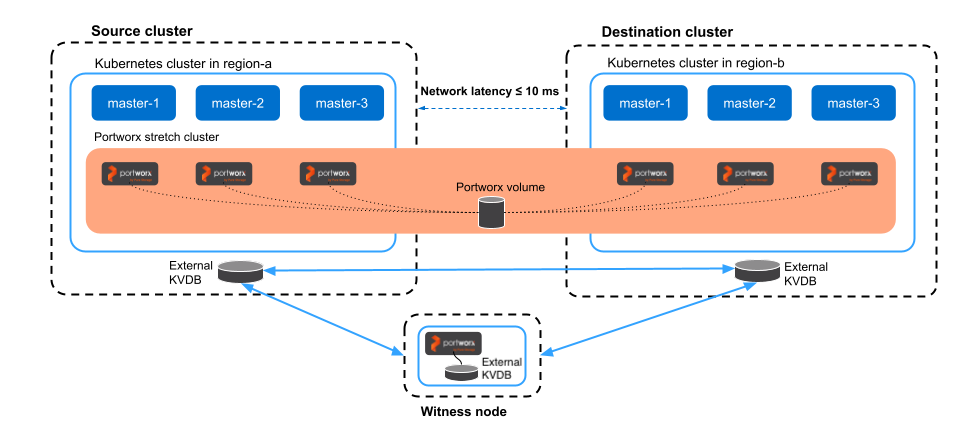
To deploy synchronous DR (also known as Metro DR) setup, you must install a single stretched Portworx cluster across two clusters. A single Portworx cluster spans across an on-premise environment with a maximum latency of 10 ms.
- Cluster-wide operators are not migrated as part of a DR migration if they are not installed in the same namespace as the applications you want to migrate (for example, in OpenShift, the operator installation defaults to the
openshift-operatorsnamespace). As a result, after migration, you will not be able to scale up or down your applications on the destination cluster usingstorkctl. - Synchronous disaster recovery for SUSE Virtualization is supported with Stork 26.1.0 or later and Portworx Enterprise 3.5.2 or later, with a limitation that forklifted VMs can’t be reverse-migrated.
- Synchronous DR is supported on the following platforms with vSphere cloud drive configurations:
- VMware vSphere Kubernetes Service (VKS)
- Vanilla Kubernetes
- OpenShift deployed on vSphere or Bare Metal
- On OpenShift Container Platform, synchronous DR is supported for:
- KubeVirt virtual machines using Portworx RWX block volumes
- Clusters using local drives on bare metal nodes
- In a Synchronous DR setup:
- The maximum supported replication factor is
2. - The sharedv4 service volumes are not supported in the Portworx cluster.
- The maximum supported replication factor is
- Synchronous DR is not supported on KubeVirt VMs with Sharedv4 service volumes.
The following diagram shows a synchronous DR setup involving two clusters in the same metropolitan area network:
Perform the following steps to set up synchronous DR:
📄 Prerequisites
Prerequisites for Synchronous DR migration.
📄 Prepare your cluster
Find out how to install a single stretched Portworx cluster across multiple Kubernetes clusters.
📄 Setup a witness node
Find out how to install a witness node.
📄 Generate and apply a cluster pair spec
Find out how to pair your clusters.
📄 Schedule a migration
Find out how to synchronize your clusters by scheduling periodic migrations between them.
📄 Failover an application
Find out how to failover an application from one Kubernetes cluster to another.
📄 Failback an application
Find out how to failback an application from the backup Kubernetes cluster to the original one.