Single data center/multiple AZ Portworx deployment options
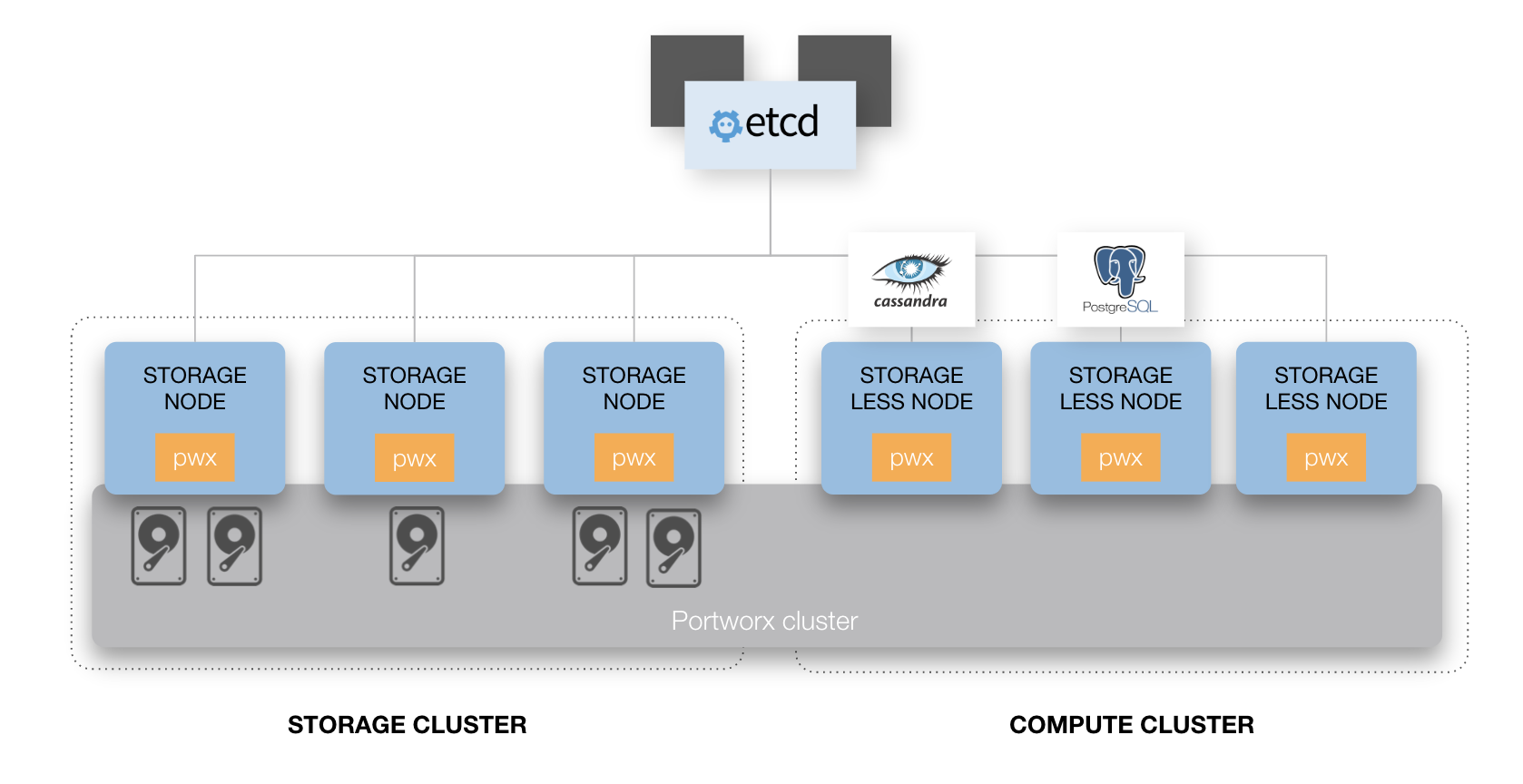
Option 1- Dedicated Portworx storage cluster
Suitable for:
- Public cloud or on-premises deployments. When deployed in the public cloud with Availability Zones or in an on-premises data center with fault domains, Portworx volumes and replicas will automatically be placed across these boundaries to maximize high availability.
Solves for these primary needs:
- Computing elasticity. You have a dynamic computing environment, where computing nodes elastically increase or decrease based on workload demand. Reasons for this might include: increasing worker nodes to handle the number of pods in the system, instance upgrades due to kernel upgrades or patches and upgrades to your orchestrator (e.g., Kubernetes)
- Separation of computing and storage. You might want to separate computing and storage clusters so that scaling and resource utilization on the storage cluster doesn’t interfere with the computing cluster and vice versa.
Key constraints:
- This is a single data center/multiple AZ architecture. For multi-data center HA or DR, this architecture can be used in combination with the architectures presented in the DR and multi-DC HA section.
- There is potential for resource contention if stateful services are grouped onto few nodes. Plan for adequate computing capacity to avoid degraded application performance due to noisy neighbors. This can be easily solved, however, by scaling additional compute nodes.
- Increased latency from the computing cluster to the storage cluster, similar to what you would experience with a SAN or cloud block storage.
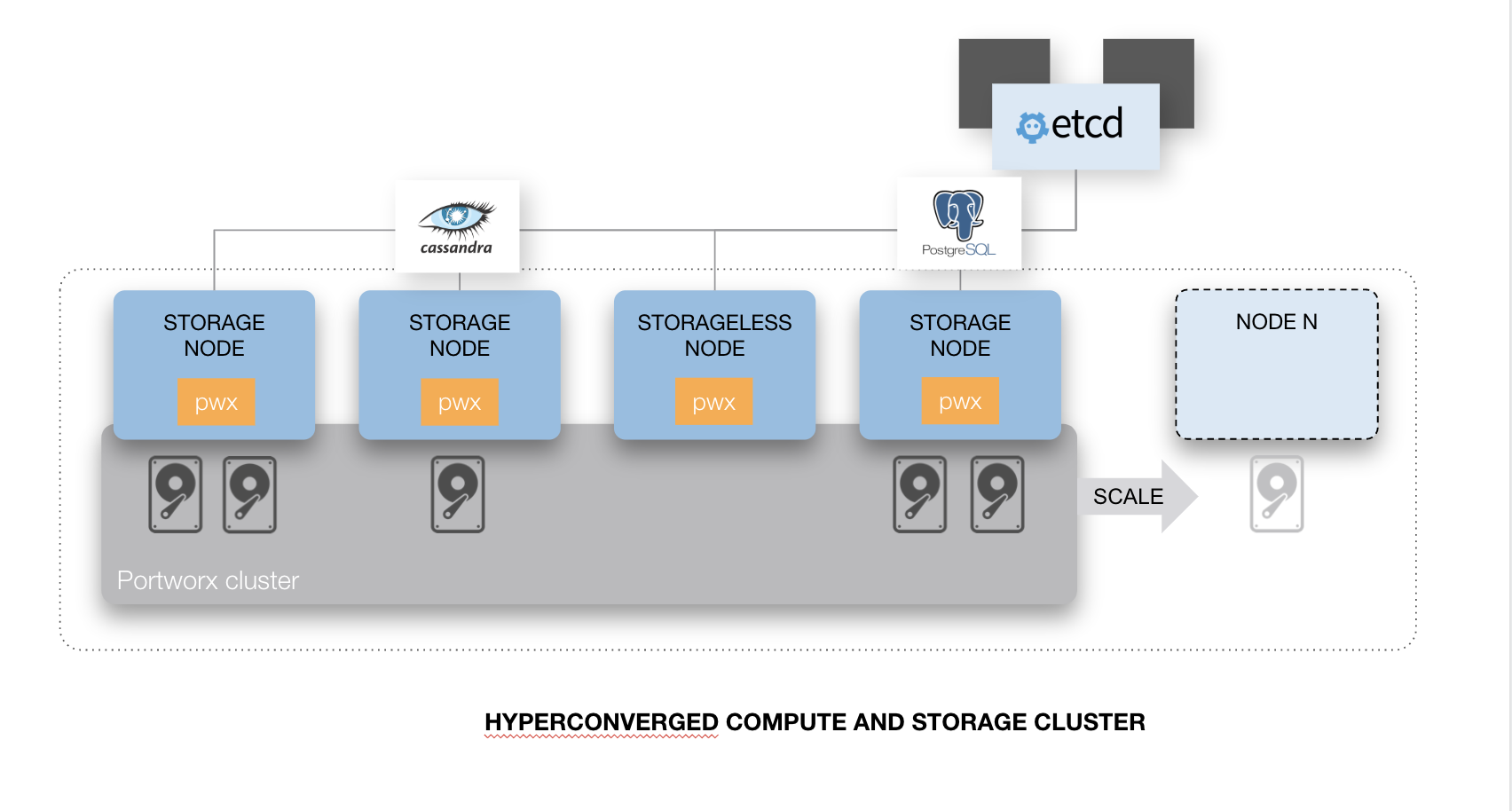
Option 2- Hyperconverged Portworx storage cluster
Suitable for:
- Public cloud or on-premises deployments. When deployed in the public cloud with Availability Zones or in an on-premises data center with fault domains, Portworx volumes and replicas will automatically be placed across these boundaries to maximize availability.
Solves for these primary needs:
- High-performance applications. Typically, this means computing and storage need to be on the same server to avoid any potential network latency.
- Cluster administrators don’t want to separately manage the computing and storage clusters.
Key constraints:
- This is a single data center/multiple AZ architecture. For multi-data center HA or DR, this architecture can be used in combination with the architectures presented in the DR and multi-DC HA section.
- VM instances are mostly static. This means the VMs don’t get recycled very frequently.
- The cluster isn’t frequently scaled horizontally. Scaling your cluster out will mean adding new compute and storage nodes each time.