Install Elasticsearch and Kibana with Portworx on Kubernetes
The following instructions are a step by step guide for deploying the Elasticsearch stack (Elasticsearch, Kibana) with Portworx on Kubernetes.
Elasticsearch is the distributed search and analytics engine that provides a unified data store for solutions built on the Elastic Stack. Refer to the Elasticsearch documentation for more details.
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster running version 1.19 or newer.
- A Portworx installation on your Kubernetes cluster. For details, see Install Portworx.
Install Elasticsearch
Portworx provides volumes to the Elasticsearch nodes, and it offers a set of storage classes for various use cases. This page uses px-csi-db for Elasticsearch pods, which creates Portworx volumes with three replicas when referenced by a volumeClaimTemplate. Refer to StorageClass Parameters for more information about StorageClass parameters that Portworx supports.
Install and deploy an Elasticsearch cluster
In this section, you will create a three node Elasticsearch cluster and a Kibana instance that are backed by Portworx volumes.
-
Install custom resource definitions:
kubectl create -f https://download.elastic.co/downloads/eck/2.4.0/crds.yamlcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/agents.agent.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/apmservers.apm.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/beats.beat.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/elasticmapsservers.maps.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/elasticsearches.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/enterprisesearches.enterprisesearch.k8s.elastic.co created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kibanas.kibana.k8s.elastic.co created -
Install the Elasticsearch Operator:
kubectl apply -f https://download.elastic.co/downloads/eck/2.4.0/operator.yamlnamespace/elastic-system created
serviceaccount/elastic-operator created
secret/elastic-webhook-server-cert created
configmap/elastic-operator created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator-view created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator-edit created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/elastic-operator created
service/elastic-webhook-server created
statefulset.apps/elastic-operator created
validatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io/elastic-webhook.k8s.elastic.co createdVerify the Operator pod status and ensure that it shows as
READY:kubectl -n elastic-system get pods -lcontrol-plane=elastic-operatorNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
elastic-operator-0 1/1 Running 0 2m42 -
Deploy an Elasticsearch cluster. Copy and save the following spec as a YAML file, changing the highlighted values as necessary:
apiVersion: elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/v1
kind: Elasticsearch
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
namespace: elastic-system
spec:
version: 8.4.3
nodeSets:
- name: node
count: 3
config:
node.store.allow_mmap: false
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: elasticsearch-data # Do not change this name unless you set up a volume mount for the data path.
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 50Gi # Change the Volumes size as required.
storageClassName: px-csi-db # Use appropriate StorageClass name.Run the following command to apply the spec:
kubectl apply -f <filename.yaml>elasticsearch.elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/elasticsearch created -
Monitor the Elasticsearch cluster until
HEALTHshows asgreenandPHASEshows asREADY:kubectl -n elastic-system get elasticsearchNAME HEALTH NODES VERSION PHASE AGE
elasticsearch green 3 8.4.3 Ready 3m21s -
To check the status of Elasticsearch pods, run the following command:
watch kubectl -n elastic-system get pods --selector='elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/cluster-name=elasticsearch'NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
elasticsearch-es-node-0 1/1 Running 0 5m
elasticsearch-es-node-1 1/1 Running 0 5m
elasticsearch-es-node-2 1/1 Running 0 5m -
To access the logs for one of the Elasticsearch node pods, run the following command:
kubectl -n elastic-system logs -f elasticsearch-es-node-0
Access your Elasticsearch cluster
Now that you've installed and deployed your Elasticsearch cluster, you're ready to access it. The deployment automatically creates a ClusterIP Service for your cluster. This example uses the service elasticsearch-es-http endpoint to provide access within the Kubernetes cluster.
-
To get the
Nameof the service and theTargetPort, run the following command:kubectl -n elastic-system describe service elasticsearch-es-httpName: <service-name>
Namespace: elastic-system
Labels: common.k8s.elastic.co/type=elasticsearch
elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/cluster-name=elasticsearch
Annotations: <none>
Selector: common.k8s.elastic.co/type=elasticsearch,elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/cluster-name=elasticsearch
Type: ClusterIP
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.104.167.40
IPs: 10.104.167.40
Port: https 9200/TCP
TargetPort: <port>/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.143.10:9200,192.168.147.138:9200,192.168.45.31:9200
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none> -
Fetch the credentials and save them as an environment variable. A default user named
elasticis automatically created with the password stored in a Kubernetes secret:ESPASSWORD=$(kubectl -n elastic-system get secret elasticsearch-es-elastic-user -o go-template='{{.data.elastic | base64decode}}') -
Access your cluster through the
elasticsearch-es-httpservice endpoint URL:kubectl exec elasticsearch-es-node-0 -n elastic-system -- curl -u "elastic:$ESPASSWORD" -k "https://<service-name>:<port>"{
"name" : "elasticsearch-es-node-2",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "3CwyPyaMREaIB-Bm8qXQ8Q",
"version" : {
"number" : "8.4.3",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "42f05b9372a9a4a470db3b52817899b99a76ee73",
"build_date" : "2022-10-04T07:17:24.662462378Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "9.3.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "7.17.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "7.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Insert and query a sample index
Insert some sample data and query the index to verify that the cluster is healthy.
-
List Elasticsearch cluster nodes:
kubectl exec elasticsearch-es-node-0 -n elastic-system -- curl -u "elastic:$ESPASSWORD" -k "https://elasticsearch-es-http:9200/_cat/nodes?v"ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role master name
192.168.143.10 35 75 1 1.90 1.85 2.42 cdfhilmrstw - elasticsearch-es-node-2
192.168.147.138 15 77 1 1.19 1.33 1.52 cdfhilmrstw - elasticsearch-es-node-0
192.168.45.31 14 77 1 1.33 1.21 1.59 cdfhilmrstw * elasticsearch-es-node-1 -
Insert a new index:
kubectl exec elasticsearch-es-node-0 -n elastic-system -- curl -XPUT -u "elastic:$ESPASSWORD" -k "https://elasticsearch-es-http:9200/customer?pretty&pretty"{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "customer"
} -
Query indexes:
kubectl exec elasticsearch-es-node-0 -n elastic-system -- curl -XGET -u "elastic:$ESPASSWORD" -k "https://elasticsearch-es-http:9200/_cat/indices?v&pretty"health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open customer VX3K32-lQxSfOYl_1dyocQ 1 1 0 0 450b 225b
See result on Portworx volumes
In this section, you will view how the Elasticsearch cluster uses Portworx volumes.
Portworx volumes are created with three replicas for storing indexes and documents for Elasticsearch. This is based on the StorageClass definition.
-
List the Persistent Volumes:
kubectl get pvNAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-7f678ca8ba07 50Gi RWO Delete Bound elastic-system/elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-2 px-csi-db 12m
pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-d1e920903be2 50Gi RWO Delete Bound elastic-system/elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-1 px-csi-db 12m
pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-c7a3e5555f41 50Gi RWO Delete Bound elastic-system/elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-0 px-csi-db 12m 45m -
List the Persistent Volume Claims:
kubectl -n elastic-system get pvcNAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-0 Bound pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-c7a3e5555f41 50Gi RWO px-csi-db 14m
elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-1 Bound pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-d1e920903be2 50Gi RWO px-csi-db 14m
elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-2 Bound pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-7f678ca8ba07 50Gi RWO px-csi-db 14m -
List the Portworx volumes:
PX_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l name=portworx -n <px-namespace> -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
kubectl exec $PX_POD -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl volume listID NAME SIZE HA SHARED ENCRYPTED PROXY-VOLUME IO_PRIORITY STATUS SNAP-ENABLED
12772348667588675 pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-7f678ca8ba07 50 GiB 3 no no no LOW up - attached on 10.13.25.240 no
1013728801369127826 pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-d1e920903be2 50 GiB 3 no no no LOW up - attached on 10.13.25.29 no
695731562422595940 pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-c7a3e5555f41 50 GiB 3 no no no LOW up - attached on 10.13.25.229 no -
Inspect one of the Portworx volumes:
kubectl exec $PX_POD -n <px-namespace> -- /opt/pwx/bin/pxctl volume inspect 12772348667588675Defaulted container "portworx" out of: portworx, csi-node-driver-registrar
Volume : 12772348667588675
Name : pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-7f678ca8ba07
Size : 50 GiB
Format : ext4
HA : 3
IO Priority : LOW
Creation time : Oct 21 00:34:10 UTC 2022
Shared : no
Status : up
State : Attached: xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-be0ef0f68452 (10.13.25.240)
Last Attached : Oct 21 00:34:34 UTC 2022
Device Path : /dev/pxd/pxd12772348667588675
Labels : namespace=elastic-system,common.k8s.elastic.co/type=elasticsearch,csi.storage.k8s.io/pvc/name=elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-2,csi.storage.k8s.io/pvc/namespace=elastic-system,elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/cluster-name=elasticsearch,io_profile=db_remote,csi.storage.k8s.io/pv/name=pvc-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-7f678ca8ba07,elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/statefulset-name=elasticsearch-es-node,pvc=elasticsearch-data-elasticsearch-es-node-2,repl=3
...
Replica sets on nodes:
Set 0
Node : 10.13.25.43 (Pool xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-9e181a790081 )
Node : 10.13.25.229 (Pool xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-64664cff557d )
Node : 10.13.25.240 (Pool xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-1cde7b129211 )
Replication Status : Up
Volume consumers :
- Name : elasticsearch-es-node-2 (xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-fe7d83266b52) (Pod)
Namespace : elastic-system
Running on : portworx-demo-node1
Controlled by : elasticsearch-es-node (StatefulSet
Install Kibana
To deploy your Kibana instance, perform the following steps.
-
Specify a Kibana instance and associate it with your Elasticsearch cluster. Copy the following spec and save it as a YAML file:
apiVersion: kibana.k8s.elastic.co/v1
kind: Kibana
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
namespace: elastic-system
spec:
version: 8.4.3
count: 1
elasticsearchRef:
name: elasticsearchApply the spec with the following command:
kubectl apply -f <filename.yaml>kibana.kibana.k8s.elastic.co/elasticsearch created -
Monitor the Kibana health and creation progress. Similar to Elasticsearch, you can retrieve details about Kibana instances:
kubectl -n elastic-system get kibanaNAME HEALTH NODES VERSION AGE
quickstart green 1 8.4.3 19h -
Watch the associated Kibana pod and wait for
READYto show1/1andSTATUSto showRunning:watch kubectl -n elastic-system get pod --selector='kibana.k8s.elastic.co/name=elasticsearch'NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
elasticsearch-kb-5f9797849f-fwk2z 1/1 Running 0 4m7s -
To see a description of the Kibana service that is automatically created for your cluster, run the following command:
kubectl -n elastic-system describe svc elasticsearch-kb-httpName: elasticsearch-kb-http
Namespace: elastic-system
Labels: common.k8s.elastic.co/type=kibana
kibana.k8s.elastic.co/name=elasticsearch
Annotations: <none>
Selector: common.k8s.elastic.co/type=kibana,kibana.k8s.elastic.co/name=elasticsearch
Type: ClusterIP
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.96.169.11
IPs: 10.96.169.11
Port: https 5601/TCP
TargetPort: 5601/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.229.144:5601
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none> -
Use the following command to access Kibana from your local workstation:
kubectl -n elastic-system port-forward service/elasticsearch-kb-http 5601 -
Open
https://localhost:5601in your browser. Your browser will show a warning because the self-signed certificate configured by default is not verified by a known certificate authority and is not trusted by your browser. You can temporarily acknowledge the warning for the purposes of this quickstart, but it is highly recommended that you configure valid certificates for any production deployments. -
Log in as the
elasticuser. Get the password with the following command:kubectl -n elastic-system get secret elasticsearch-es-elastic-user -o go-template='{{.data.elastic | base64decode}}';echo
Verify Kibana Installation
Insert data into Elasticsearch and verify that Kibana is able to search for the data in Elasticsearch. This will help create dashboards and visualizations.
-
Download a sample file named
accounts.json:kubectl exec elasticsearch-es-node-0 -n elastic-system -- curl -k -XGET "https://docs.portworx.com/portworx-enterprise/samples/k8s/efk/accounts.json?raw=true" -o accounts.json -
Insert the data into Elasticsearch:
kubectl exec elasticsearch-es-node-0 -n elastic-system -- curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -XPUT -u "elastic:$ESPASSWORD" -k "https://elasticsearch-es-http:9200/bank/_bulk?pretty&refresh" --data-binary "@accounts.json" -
To retrieve high-level information about each index in your Elasticsearch cluster, enter the following command:
kubectl exec elasticsearch-es-node-0 -n elastic-system -- curl -XGET -u "elastic:$ESPASSWORD" -k "https://elasticsearch-es-http:9200/_cat/indices?v&pretty"health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open bank rjUKwlOKRdeSQmH_29bR4Q 1 1 1000 0 754.6kb 383.9kb
green open customer VX3K32-lQxSfOYl_1dyocQ 1 1 0 0 450b 225bOnce you have run the above command you should see
bankandcustomerindexes in your Elasticsearch cluster. Search for the indexes through your Kibana dashboard. -
Log in to the Kibana dashboard using the instructions from the previous section.
-
Open the left menu and click Discover.
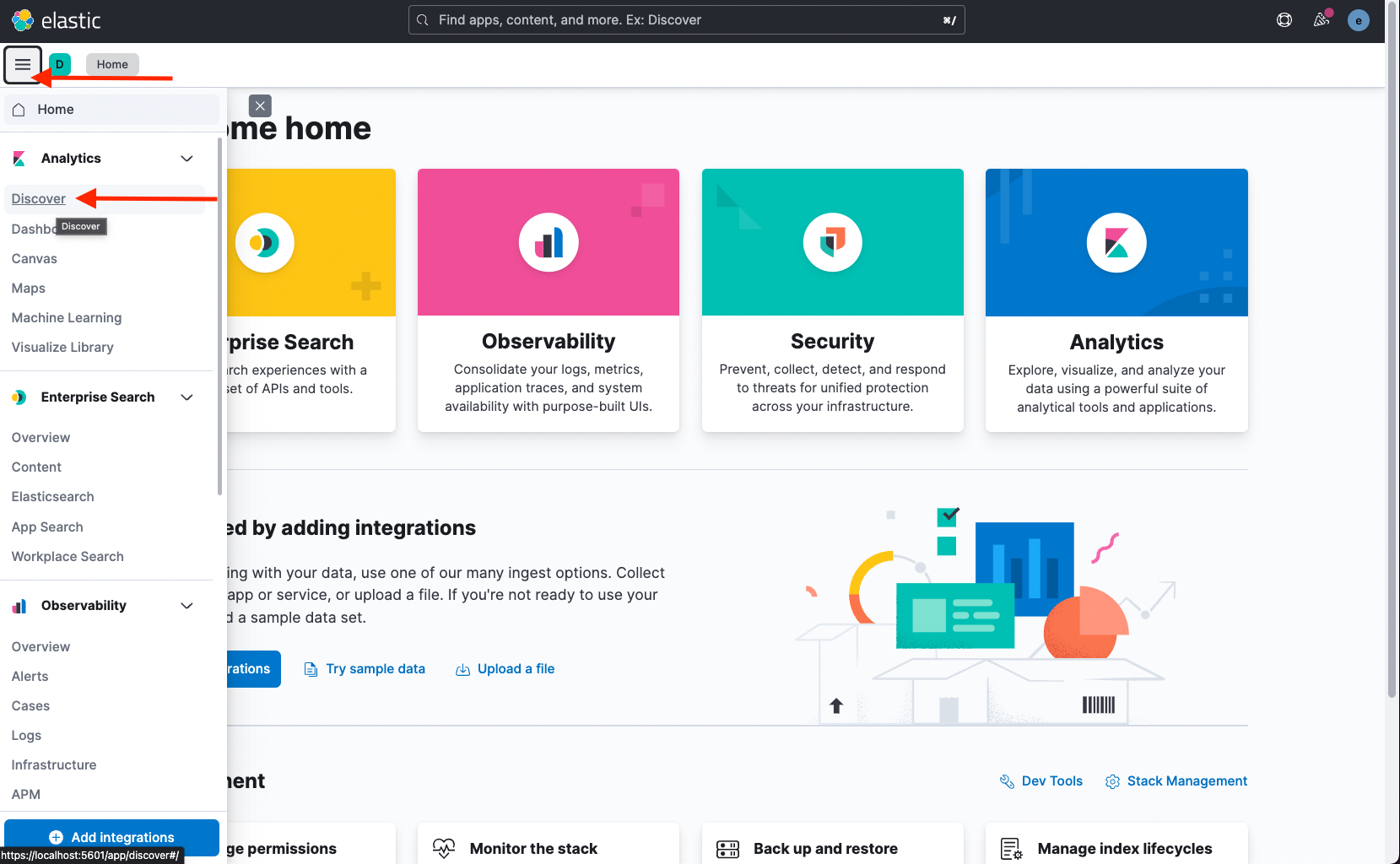
-
Click Create data view to add an index:
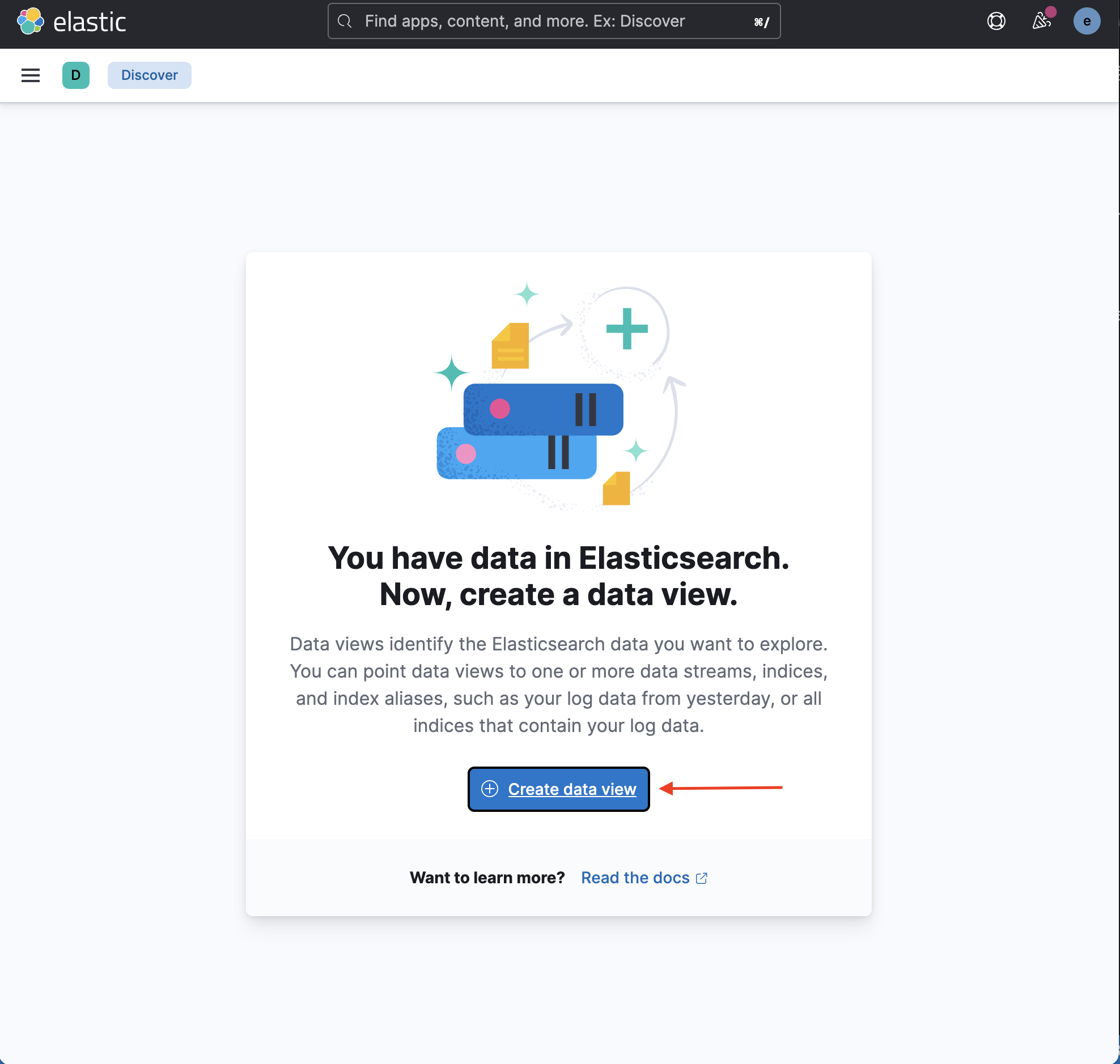
-
Provide the index pattern bank* and click Save data view to Kibana:
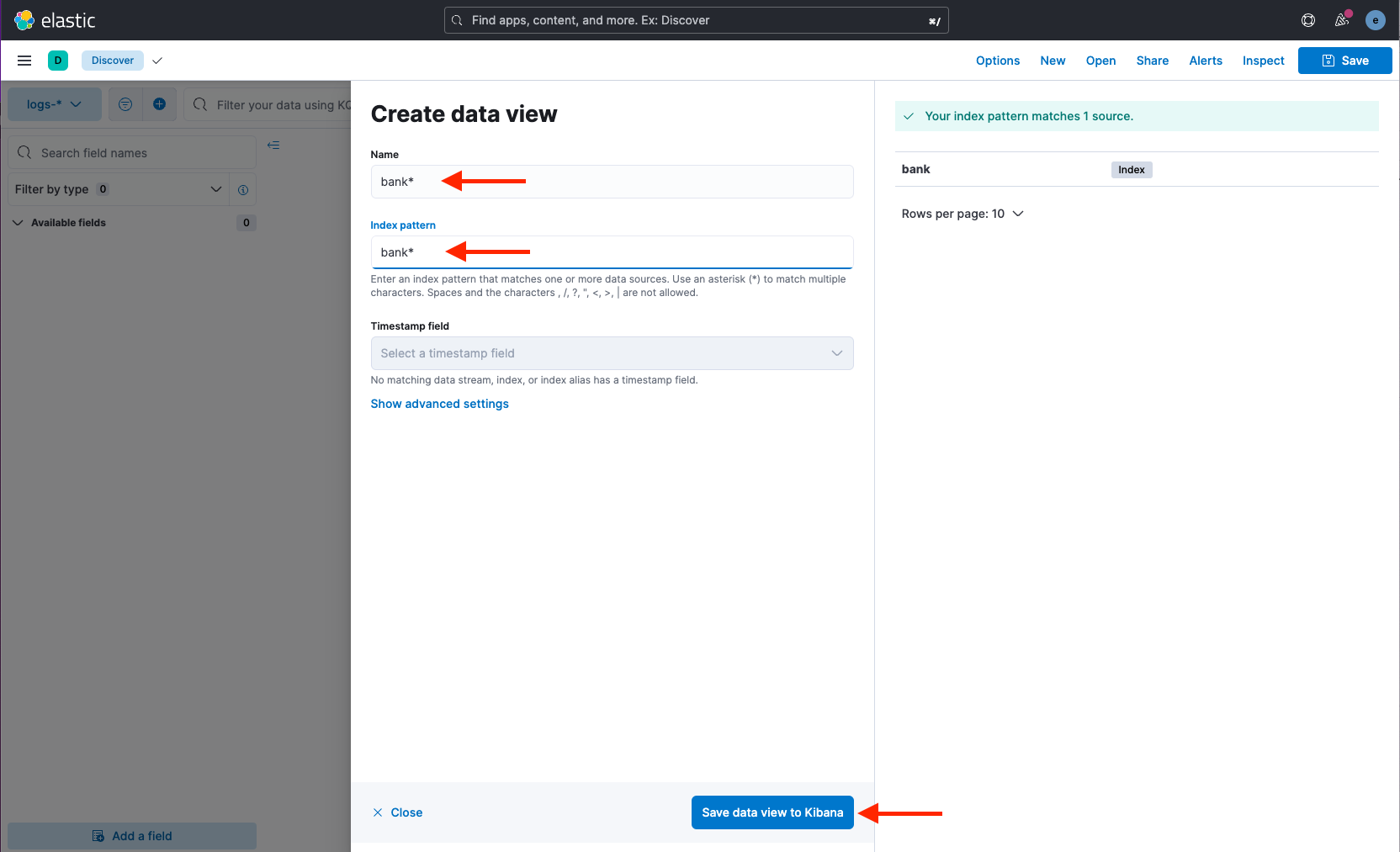
-
Select the index bank* from the data view:
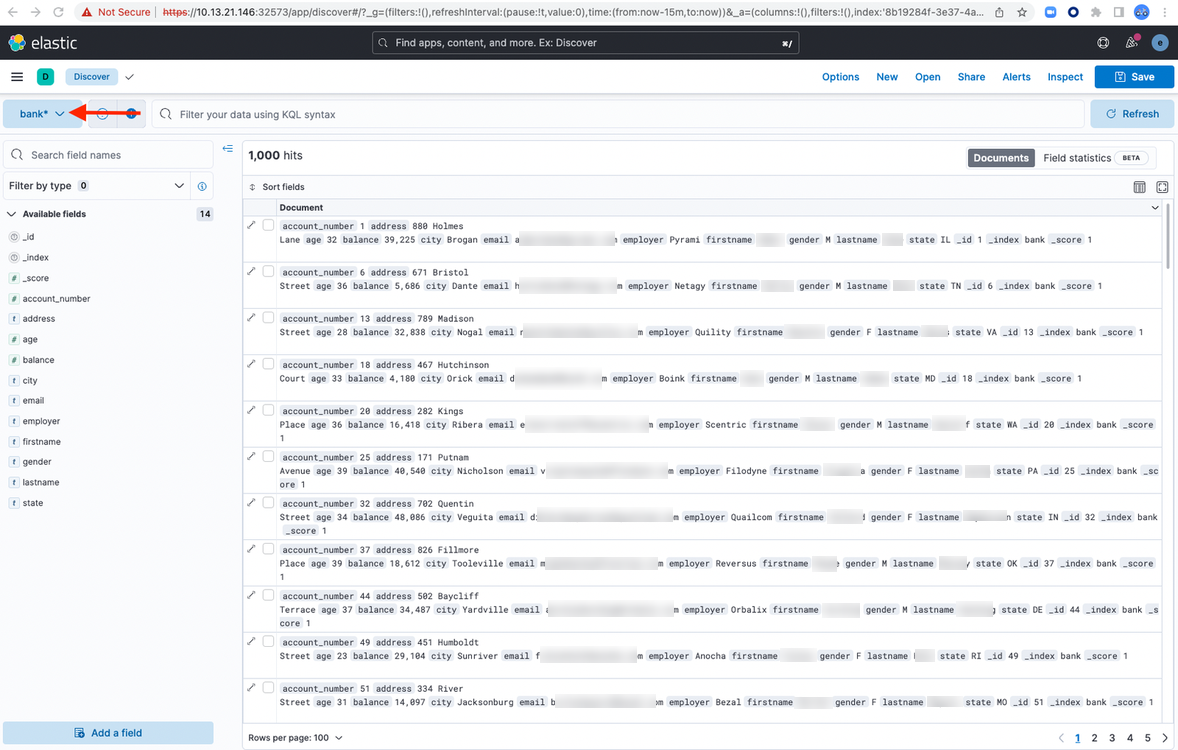
Discussion Forum
If you have more questions about this application, please head over to our discussion forum and feel free to ask more questions.